Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
小林 泰彦; 舟山 知夫; 和田 成一; 古澤 佳也*; 青木 瑞穂*; Shao, C.*; 横田 裕一郎; 坂下 哲哉; 松本 孔貴*; 柿崎 竹彦; et al.
宇宙生物科学, 18(4), p.235 - 240, 2004/12
銀河宇宙線のように、低フルエンス・低フルエンス率の高LET重イオン(粒子線)による生物影響を明らかにするためには、マイクロビームを用いた細胞照射実験が有効な手段となる。そこで、高エネルギー重イオンマイクロビームを顕微鏡観察下の生物試料に照射するために原研・高崎研・バイオ技術研究室で開発した細胞局部照射装置を用いて、哺乳動物培養細胞を個別に重イオンで照射・観察する実験系を開発した。標的細胞を貫通したイオンのエネルギーと個数をシンチレータ/フォトマルを用いて測定することによって、重イオンを1個ずつカウントしながら正確に照射することが可能となった。さらに、CR-39を直ちに37 Cでエッチングして各標的細胞における実際のイオン飛跡を可視化すると同時に、その飛跡が可視化されたCR-39上で細胞の照射後培養と観察を継続する方法を確立した。国内外の重粒子線のマイクロビーム開発の歴史を概観し、細胞核へのシングルイオンヒット効果やバイスタンダー効果に関する最近の研究成果をレビューする。
Cでエッチングして各標的細胞における実際のイオン飛跡を可視化すると同時に、その飛跡が可視化されたCR-39上で細胞の照射後培養と観察を継続する方法を確立した。国内外の重粒子線のマイクロビーム開発の歴史を概観し、細胞核へのシングルイオンヒット効果やバイスタンダー効果に関する最近の研究成果をレビューする。
小林 泰彦; 舟山 知夫; 和田 成一; 坂下 哲哉
宇宙生物科学, 18(3), p.186 - 187, 2004/11
銀河宇宙線のように、低フルエンス率の高LET重イオン(粒子線)による生物影響を明らかにするためには、マイクロビームを用いた細胞照射実験が有効な手段となる。そこで、原研・高崎研・バイオ技術研究室で開発した細胞局部照射装置を用いて、哺乳動物培養細胞を個別に重イオンで照射し、その影響を経時的に観察する実験システムを開発している。今回、照射前に試料を自動スキャンして細胞を検出するオフライン顕微鏡及び取得した座標データに従ってビーム位置に標的細胞を移動するオンライン顕微鏡の各々の試料ステージ更新し、従来は 10
10 m以上の誤差があった試料移動の位置再現精度が
m以上の誤差があった試料移動の位置再現精度が 1
1 mに向上したことにより、多数の標的細胞を次々に自動照準して連続的にシングルイオン照射することが可能になった。併せて、最近の細胞照射実験結果について報告する。
mに向上したことにより、多数の標的細胞を次々に自動照準して連続的にシングルイオン照射することが可能になった。併せて、最近の細胞照射実験結果について報告する。
服部 佑哉; 横谷 明徳; 渡辺 立子
no journal, ,
低線量放射線が全体に照射された細胞集団では、放射線が当たっていない細胞(非照射細胞)が存在し、細胞間のシグナル伝達により、非照射細胞にも細胞死等の放射線応答が現れる。本研究では、低線量の放射線応答に対する細胞間シグナル伝達の影響を調べることを目的とする。そのために、細胞間シグナル伝達を考慮した細胞集団の放射線応答モデルを用いて、高線量放射線を照射した実験データを基に、細胞間シグナル伝達に起因する細胞の生存率を推定する。本研究で用いる放射線応答モデルでは、細胞集団を格子で分割し、1細胞を1格子とした2次元平面で表現する。放射線のヒット数は、格子ごとに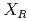 で与える。細胞間シグナルの格子内濃度は、培養液経由シグナルの濃度
で与える。細胞間シグナルの格子内濃度は、培養液経由シグナルの濃度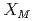 、ギャップ結合経由シグナルの濃度
、ギャップ結合経由シグナルの濃度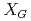 とし、拡散方程式に基づいて格子間を伝達する。個々の細胞の細胞周期は、周期的な進行(G1, S, G2, M期)が放射線のヒット
とし、拡散方程式に基づいて格子間を伝達する。個々の細胞の細胞周期は、周期的な進行(G1, S, G2, M期)が放射線のヒット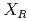 とシグナル
とシグナル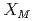 ,
, 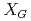 によって一時停止する仮想時計として表現する。格子内の
によって一時停止する仮想時計として表現する。格子内の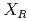 ,
, 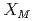 ,
, 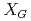 が閾値
が閾値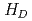 を超えたとき、その格子の細胞の状態を細胞死とする。モデルを用いて、高線量の放射線照射シミュレーションを実施した結果、細胞の生存率に対する線量依存性について、実験データと同じ傾向が確認できた。発表では、細胞間シグナル伝達の有無による生存率の変化とシミュレーションによって推測した低線量放射線を照射した細胞集団の生存率を報告する。
を超えたとき、その格子の細胞の状態を細胞死とする。モデルを用いて、高線量の放射線照射シミュレーションを実施した結果、細胞の生存率に対する線量依存性について、実験データと同じ傾向が確認できた。発表では、細胞間シグナル伝達の有無による生存率の変化とシミュレーションによって推測した低線量放射線を照射した細胞集団の生存率を報告する。
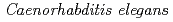
鈴木 芳代; 坂下 哲哉; 服部 佑哉; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
We recently found that whole body irradiation reduced locomotion in 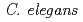 , though the mechanisms are not clear. It is well known that free radicals such as OH
, though the mechanisms are not clear. It is well known that free radicals such as OH and H
and H are produced following exposure of ionizing radiation. The reactions of free radicals cause the production of oxidative stress including hydrogen peroxide (H
are produced following exposure of ionizing radiation. The reactions of free radicals cause the production of oxidative stress including hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ). Oxidative stress is known as an important factor of aging, and may relate to the decrease of motility observed in the aging process. We therefore explored the potential effectiveness of H
). Oxidative stress is known as an important factor of aging, and may relate to the decrease of motility observed in the aging process. We therefore explored the potential effectiveness of H O
O in the suppression of
in the suppression of 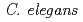 's locomotion. Wild-type animals were exposed to graded doses of H
's locomotion. Wild-type animals were exposed to graded doses of H O
O and the locomotory rate was evaluated. The locomotory rate was significantly decreased in H
and the locomotory rate was evaluated. The locomotory rate was significantly decreased in H O
O -exposed animals, in which the dose response was similar to that in the irradiated animals. We subsequently investigated the radiation effects on the pharyngeal pumping motion (chewing and swallowing) and the involvement of oxidative stress. As a result, the proportion of the pumping-motion arrest significantly increased after whole body irradiation and the pumping-motion arrest was restored within several hours. Furthermore, the response in H
-exposed animals, in which the dose response was similar to that in the irradiated animals. We subsequently investigated the radiation effects on the pharyngeal pumping motion (chewing and swallowing) and the involvement of oxidative stress. As a result, the proportion of the pumping-motion arrest significantly increased after whole body irradiation and the pumping-motion arrest was restored within several hours. Furthermore, the response in H O
O -exposed animals was similar to that in the irradiated animals. These results support the possibility that radiation-induced suppression of both locomotion and pumping motion in
-exposed animals was similar to that in the irradiated animals. These results support the possibility that radiation-induced suppression of both locomotion and pumping motion in 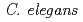 was caused by radiation-produced H
was caused by radiation-produced H O
O .
.
泉 雄大; 山本 悟史*; 藤井 健太郎; 横谷 明徳
no journal, ,
In a unit chromatin architecture of eukaryotic cells, DNA wraps around histone proteins. It has been gradually recognized that chemical modifications of histones play important roles in DNA repair processes. Kinds of modifications and the functions of modified histones are widely studied, but the conformation of modified histone has not been studied well. In this work, we investigated the secondary structural change of histone H2A/H2B induced by X-ray irradiation to living cells, measuring circular dichroism (CD) spectra. The CD spectra show that  -helix structure relatively increased in the X-irradiated cells. The secondary structural change would be induced by chemical modifications of histone H2A/H2B. This structural change may also play important roles in DNA repair processes.
-helix structure relatively increased in the X-irradiated cells. The secondary structural change would be induced by chemical modifications of histone H2A/H2B. This structural change may also play important roles in DNA repair processes.

鈴木 芳代; 坂下 哲哉; 服部 佑哉; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
Oxidative stress such as hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) has been identified as one of the important factors in aging, and this may be related to the decrease in motility observed during the aging process. In the present study, we therefore explored the potential effectiveness of H
) has been identified as one of the important factors in aging, and this may be related to the decrease in motility observed during the aging process. In the present study, we therefore explored the potential effectiveness of H O
O in the suppression of
in the suppression of  ' locomotion (crawling). Young adult wild-type animals were exposed to S-basal buffer containing graded doses of H
' locomotion (crawling). Young adult wild-type animals were exposed to S-basal buffer containing graded doses of H O
O . Exposure to H
. Exposure to H O
O induced reduction of locomotion similar to that observed after whole-body irradiation. To investigate the radiation effects and the involvement of oxidative stress on other types of movement, we subsequently focused on the pharyngeal pumping motion (chewing and swallowing). The proportion of animals in which the pumping motion has stopped immediately after H
induced reduction of locomotion similar to that observed after whole-body irradiation. To investigate the radiation effects and the involvement of oxidative stress on other types of movement, we subsequently focused on the pharyngeal pumping motion (chewing and swallowing). The proportion of animals in which the pumping motion has stopped immediately after H O
O exposure increased. This response was similar to that of irradiated animals. These results support the possibility that radiation-induced suppression of both locomotion and pumping motion in
exposure increased. This response was similar to that of irradiated animals. These results support the possibility that radiation-induced suppression of both locomotion and pumping motion in  was caused by radiation-produced H
was caused by radiation-produced H O
O . In this presentation, we will give an outline of the radiation effects on
. In this presentation, we will give an outline of the radiation effects on  and discuss the involvement of the radiation-induced oxidative stress in the phenomena.
and discuss the involvement of the radiation-induced oxidative stress in the phenomena.